In this lecture I learnt that everything I once knew about colour was now wrong and it was all about how we perceive colour.
We started off the lecture going over some things that we had learnt in school and some we weren't familiar with for example:
-White light is made up of colour, each colour has a different wavelength.
-In the eyeball the rods let us see tone (light/dark) and the cones let us see colour.
-We have 3 cones-1 red, 1 green and 1 blue
-We see the colour when it hits the corresponding cone.
-Yellow is seen by a combination of the red+ green cones being hit.
If there's no light, is there no colour?
Then we looked at people that are colour blind and saw that they see things in different colours. Deuteranopia causes you to see everything in yellows and tritanopia makes you see everything in pinks and blues.
-The primary colours are blue red and yellow.
-mixing primary's gives you secondaries
-complimentary colours are opposites on the colour wheel
-complementaries are made up of the other 2 primaries.
-Complementaries remove colour from each other and become a neutral grey.
-neutral colour wheel= tertiaries- pure colour mixed in different ways
-spectral colour- perception of colour in different light
-yellow cannot be a spectral colour
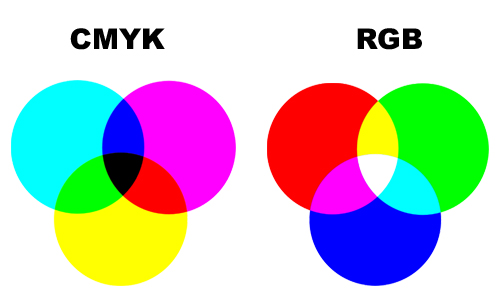
The two colour modes are made up of each other. Notice how the overlapping of the cmyk colours makes the rgb colours and visa versa.
-Subtractive colour is physical- mixing colours turns to black.
-Additive colour is on screen where mixing colours turns them white.
Dimensions of colour
-chromatic value= tone, saturation and hue
-shades= pure colour getting darker
-Tint= pushing toward white
-Tone= combination of shade and tint.
-Luminance- how bright+ pure the colour is
-Bright= reflecting light
-Dark= absorbing light
-desaturation= taking purity away, removing colour, making darker, turning into a different colour
We perceive colour by what's around it. We are fooled into seeing colours. The colour changes by comparing another colour to it. you may see something as red until you put something more red next to the original colour. Now the original looks more pink or orange.
This is why we need a system so we get the exact right colour. The most common system is Pantone. These have numbers and letters with every colour under the sun. Colours are only the colour they are by concencous and even that cant be trusted.
Colour and contrast
-Contrast of tone. monochromatic, light value and dark value
-Contrast of hue- the greater the distance between hues on the colour wheel, the bigger the contrast
-Contrast of saturation
-contrast of proportion
-contrast of temperature- putting colours together and adding cold and hot changes the appearance of the colour.
-non existing gradients because of temperature contrast
-complimentary contrast
-simultaneous contrast- all contrasts working together
Subjective colour
The primary colour wants it's complimentary colour to be there so when we see blue on grey, the grey looks yellow orange or brown.
same as yellow on grey makes the grey look purple.


No comments:
Post a Comment